Role management
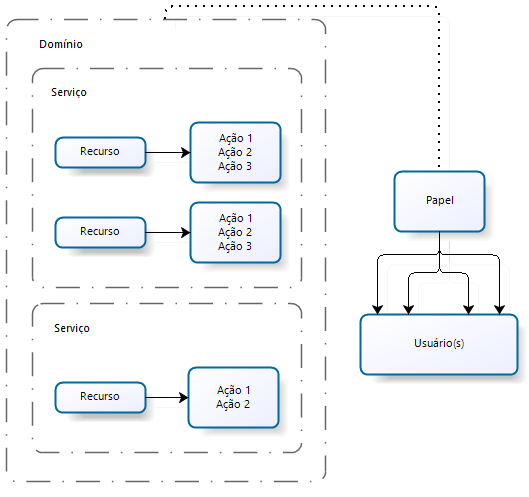
Role management is the mechanism responsible for ensuring that only authorized users consume protected platform resources. In other words, controlwhat a user can access and perform. Permissions are organized into domains, services, and resources that have actions. Thus, roles are assigned a set of permissions and users are related to these roles.
- Domain: it is the first level of organization of permissions and a way of grouping one or more services, being a logical and not a physical concept. For example, "platform" domain to indicate technology services, or "HCM" to indicate a module or management of a product;
- Service: is the second level of permissions, composed of elements that implement a set of functionality in a domain. For example: "cash flow" as responsible for the entry and exit of financial resources from a company;
- Resource: a resource is any computational item that requires some access control. For example: registrations, processes, reports, screens, etc.
- Action: is any operation that can be performed on a resource. For example: for a report, there are the actions of Create, Edit, Delete, Generate and Print. An action can be something very particular to a resource, as in the case of a Point Registration resource, which can present the Make Settlement action.
There are some native features and actions that are available when deploying the senior X Platform, however, there are no native or pre-defined roles available. Furthermore, in the concept of permission it is not possible to prevent a role from performing a certain action, but rather not to give it permission.
Combination of permissions
The user joão.silva is related to the collaborator role. This role has authorization to perform the Query action on the custom field resource.
The user pedro.santos is related to the collaborator and analyst role. In addition to the Contributor role definitions (above), the Analyst role has Create, Edit, and Delete permissions in the custom field feature.
The user maria.silva has the roleadmin, which does not contain any filters, that is, it does not impose specific restrictions. Therefore, a user with the roleadmin has visibility of all companies and branches. However, when adding an additional role such asbranch administrator 1 (which filters company 1 with branch 1), the system starts to apply restrictions according to the filters for that specific role (limiting the information to company 1 with branch 1), even with the presence of the most comprehensive role.
If a third role is added, for example, with a filter for company 2 with branch 2, the system must take all roles into account, resulting in a filter that includes company 1 with branch 1 and company 2 with branch 2.
Denial of permission
The user rosa.maria is only related to the analyst role; Because the analyst role has Create, Edit, and Delete permissions on the custom field resource, but does not have Query permission, this user will not be able to perform custom field queries.
Types of permissions
On the senior X Platform there are types of permissions that have the benefits of being scalable, flexible and auditable. Are they:
The RBAC (Role-Based Authorization Control) is a role-based permissions control. It is the first level of access permissions and also the simplest. Simply inform which resources a role can access and which actions can be performed on each resource.
It is possible that there are needs beyond what RBAC provides, which is why the concept of ABAC was created.
Complementing RBAC, authorization can be carried out through attribute validation. During resource definition, the business service can link attributes, making validation possible during authorization verification. When the resource has attributes, during permissions management, the end user can include ascript (javascript) which must validate the attributes, thus allowing or denying access.
On the senior X Platform, ABAC is used for more complex permissions, such as time of day and the user's geographic location, to allow the system to be used in a dynamic and distributed way.
For more complex authorization management, filters can be linked to permissions or roles so that business services can allow partial access to a resource/action. Like ABAC, existing filters are defined by the business service, without user interaction. For example, a given role can only access invoices issued by the company to which it is associated, or it can only access data from company X, branch X.
The platform currently allows you to define two types of filters:
- Resource filter: resource or boolean filters are linked to actions during permissions management to activate or deactivate a functionality, for example: the user resource with View action returns a list of all users and has the restrict branch filter. During permission management, I can add the filter in the manager role, but not in the director role, as the director can view users from all branches.
- Service filter: they are more complex than resource filters, as they allow you to add a set of values linked directly to the role and service of the resource in question. Following the previous example, the user resource with View action returns a list of all users and has the branch code filter. Given that a manager belongs to a branch and a regional manager to one or more branches, I can add the filters as follows:
| Branch Manager Role 1: Filter with code 1 |
| Regional Manager Role 1: Two sets of filters, one code 1 and one with code 2 |
Once linked to the role, the filters will be returned upon permission verification so that the business can consume this data.
Observation
The senior X platform has a default cache time to apply filters to the database. The current default cache time is10 minutes — this is the response time until a new coverage filter registered on paper takes effect for users.
Managing roles
Roles are used to associate a user with a position within the organization or activity that will be performed. They are the essence of user management, as their architecture must support business rules at different levels of access permission.
Remember to configure a role so that you can apply it to multiple users. Prefer to create roles with functionalities that belong to the same domain, this way it will be simpler to manage your company's permissions.
Important
Only users who have administrator permission can make other users administrators (admin role).
It is not allowed to assign a role to your own user, the assignment must be granted by another user.
What do you need to do:
- Access Technology > Administration > Authorization > Paper management;
- click inNew role;
- Inform thePaper name and theRole Description to identify you;
- On the Users tab, select the users who will be part of the role:
- Find the user you want to include in the role and use the
- toggle from the Associate
- On the Permissions tab, select the features and actions that users associated with the role will have ac
- cess to:
- Click on a domain/service to view the resources and actions contained therein
- ;Click the check box to define the role's resources and access;Some resources may have filters, which will be displayed next to the action. By clicking on them you can create Boolean filters;
- On the Filters tab, view the domains/services that have custom filters and define one or more sets of values, with each page being a set:
- Click on a dom
- ain/service;
- Enter the filter v
- On the Properties tab, add a set of keys/values for a role, assigning it metadata that can be used in customizations:
- addName and then set the Value
- ;
- In the tabapplications, select the access applications that will be part of the role:
- Find the application you want to include in the paper and usetoggle of the associated column.
- If you have roles created in the X Solutions Platform, and intend to integrate a role with the same name registered in G5/LDAP, thetoggle must be checked, this way the integrator has permission to edit the existing role. If you do not check, the message will be displayedthe paper already exists and will not be integrated until the user corrects the names.
- After configuring the role, click save.
- Access Technology > Administration > Authorization > Paper management;
- Locate the role you want to change;
- click inTo edit;
- Make the necessary changes;
- click inTo save.
At any time clickCancel to discard the changes.
- Access Technology > Administration > Authorization > Paper management;
- Locate the role you want to delete;
- click inTo edit;
- click inDelete;
- Confirm the deletion.
At any time clickCancel to discard the changes.
Duplicating a role makes it easier to create a new role that has similar permissions to another role. When duplicated, it creates a new role with the same permissions. However, users associated with the role will not be copied to the duplicate role.
- Access Technology > Administration > Authorization > Paper management;
- Locate the paper you want to duplicate;
- click inTo edit;
- click inDuplicate;
- Inform thePaper name It isDescription the role that will be created;
- click inTo save to confirm the operation.
At any time clickCancel to discard the changes






